Plant Physiology 160: 1551-1566 (2012)
Distinct cell wall architectures in seed endosperms in representatives of the Brassicaceae and Solanaceae [W][OA]
Centre for Plant Sciences, Faculty of Biological Sciences, University of Leeds, Leeds LS2 9JT, UK (KL, PK)
Wageningen Seed Lab, Laboratory of Plant Physiology, Wageningen University, Droevendaalsesteeg 1, 6708 PB, Wageningen, The Netherlands (BD, LB)
Department of Molecular Plant Physiology, Utrecht University, 3584 CH Utrecht, The Netherlands (BD, LB)
University of Freiburg, Faculty of Biology, Institute for Biology II, Botany/Plant Physiology, D-79104 Freiburg, Germany (TS*, GLM*)
ARC Centre of Excellence in Plant Cell Walls, School of Botany, University of Melbourne, Parkville, Victoria 3010, Australia (BD, LB)
* Current Address: School of Biological Sciences, Royal Holloway, University of London, Bourne Building 3-30, Egham, Surrey, TW20 0EX, UK
Received July 13, 2012; Accepted September 4, 2012; Published September 6, 2012.
DOI:10.1104/pp.112.203661
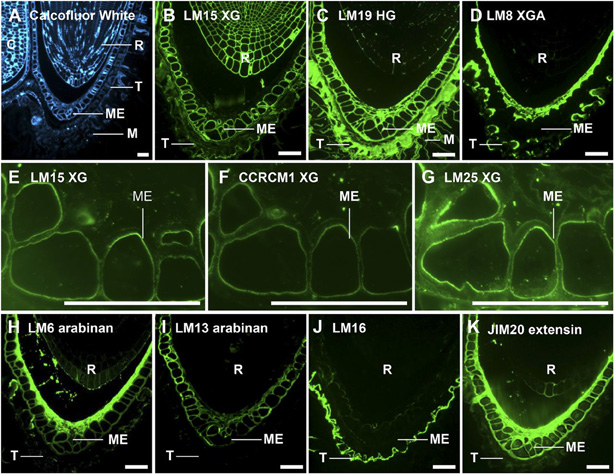
Figure 4. In situ localization of cell wall epitopes in medial longitudinal sections of 3-h-imbibed Lepidium seeds.
A, Calcofluor White labeling of Lepidium showing cotyledons (C), radicle (R), testa (T), ME, CE, and PE.
B, The LM15 XG epitope was uniformly distributed in embryo cell walls.
C, LM19 bound strongly and uniformly to endosperm, testa, and mucilage.
D, The LM8 epitope was restricted to the inner face of the endosperm and surface of the testa.
E and F, The LM15 XG and CCRCM1 XG epitopes were restricted to the inner wall in the endosperm.
G, A related XG probe LM25 bound more extensively than LM15 and CCRCM1. CCRCM1 and LM25 both bound strongly to embryo cell walls.
H and I, Localization of cell wall arabinans using LM6 and LM13 revealed spatial heterogeneity; the LM6 epitope was most abundant at the inner face of the endosperm, while LM13 bound more uniformly to endosperm walls.
J, LM16 strongly labeled the testa surface and weakly labeled endosperm cell walls.
K, Extensin recognized by JIM20 was abundant in the endosperm and at the inner face of the ME. Bars = 50 mm.
| Article in PDF format (1.5 MB) Supplementary data file (2 MB) |
|
|
|
The Seed Biology Place |
Webdesign Gerhard Leubner 2000 |