Zeitschrift für Naturforschung 49c:
781-790 (1994)
Phenylalanine analogues: Potent inhibitors of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase
are weak inhibitors of phenylalanine-tRNA synthetases
Received: 15 July 1994
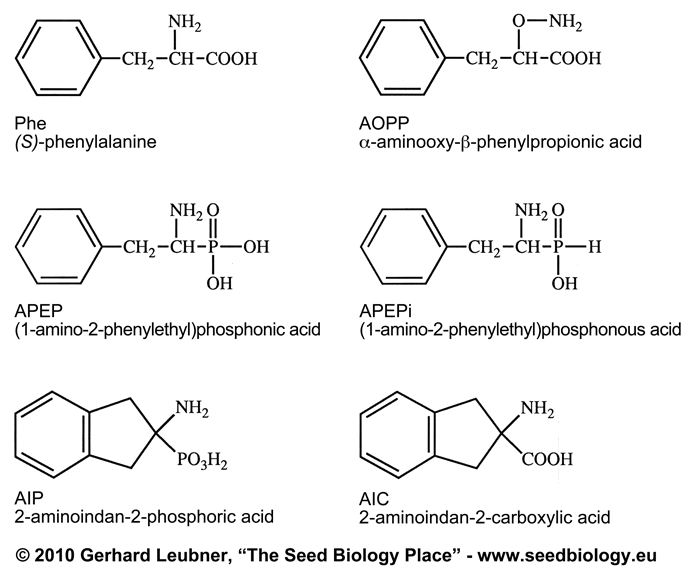
Abstract. (1-Amino-2-phenylethyl)phosphonic acid (APEP),
(1-Amino-2-phenyl-ethyl)phosphonous acid (APEPi), alpha-aminooxy-ß-phenylpropionic
acid (AOPP) and several other phenylalanine analogues are potent inhibitors
of (S)-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) in vitro and in vivo. The ability
of these compounds to inhibit (S)-phenylalanine-tRNA synthetases (PRSs)
from wheat germ, soybean, and baker's yeast is investigated and compared
to the inhibition of PAL. We have found APEP and APEPi to inhibit the tRNAphe-aminoacylation
reactions catalyzed by the three PRSs studied in vitro in a competitive
manner with respect to (S)-phenylalanine. (R)-APEP inhibits the PRSs with
apparent Ki values of 144 µM for wheat germ (apparent Km for (S)-phenylalanine
5.2 µM), 130 µM for soybean (apparent Km for (S)-phenylalanine
0.9 µM), and 1096 µM for baker's yeast (apparent Km for (S)-phenylalanine
5.5 µM). The apparent Ki values for (R)-APEPi are 315 µM, 160
µM, and 117 µM, respectively. APEP and APEPi inhibit the ATP-pyrophosphate
exchange reactions catalyzed by the PRSs from wheat germ and baker's yeast,
but they can not be activated and serve as substrates in these reactions.
AOPP has no affinity to any of the three PRSs, whereas it is a potent inhibitor
of PAL. In light of our in vitro results with PRSs from different sources
it appears unlikely that the PAL inhibitors we have studied have any significant
inhibitory effect on the initial step of protein synthesis in vivo.
Key words: Phenylalanine Analogues, Inhibitors, Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase,
Phenylalanine-tRNA Synthetase
Hyperlink to: Appert, Zon, Amrhein (2003) Phytochemistry 62: 415-422
Kinetic analysis of the inhibition of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase by 2-aminoindan-2-phosphonic acid and other phenylalanine analogues
Phenylalanine analogues that are inhibitors of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase
| Article in PDF format (4.4 MB) | Abstract Fig. 1 Fig. 2 Tab. 1 Tab. 2 Tab. 3 Tab. 4 Phe-analogues |
|
|
The Seed Biology Place
|
Webdesign Gerhard Leubner 2000
|